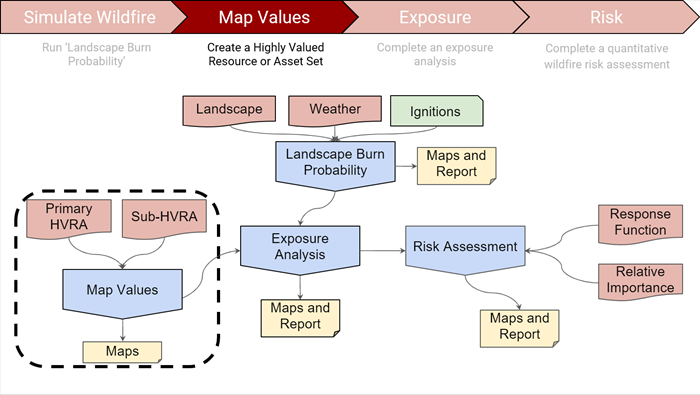
About Map Values - Highly Valued Resources or Assets (HVRAs)
Introduction
Map Values allows you to create a consolidated spatial layer of HVRAs (HVRA Set) consisting of the values you select. Overlaying HVRA Sets with model outputs in Map Studio enables quick qualitative assessment of modeled fire behavior in relation to your mapped values. HVRA Sets can be overlaid with model outputs, or used as part of a larger assessment. How you plan to use the HVRA Set should dictate what you include in the Set. Once you build an HVRA Set in IFTDSS it is saved in your Workspace and is available throughout IFTDSS.
HVRA Sets are required to run an Exposure Analysis. An Exposure Analysis (EA) summarizes Landscape Burn Probability outputs across your HVRA Set. An EA is necessary to conduct a Quantitative Wildfire Risk Assessment (QWRA) which allows you to calculate risk (an estimate of the benefits or losses) based on Landscape Burn Probability model outputs.
Defining Map Values and HVRA Sets
Values on the landscape are things that we care about, natural resources or human-made assets for example. In IFTDSS, the term “value” refers specifically to Highly Valued Resources or Assets (HVRAs).
-
Highly Valued Resources or Assets (HVRAs) are landscape features that are influenced positively and/or negatively by fire. Resources are naturally occurring, while Assets are human-made.
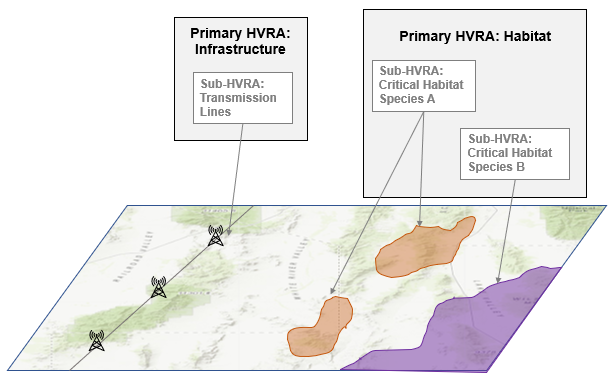
HVRAs are categorized by Primary and Sub-HVRAs:
- Primary HVRAs are the overall categories into which the Sub-HVRAs are sorted. For example, “habitat” can be the Primary HVRA, with Sub-HVRAs defined as the habitat for individual species.
-
Sub-HVRAs are the geospatial component of Primary HVRA category. For example, “powerlines” can be considered a Sub-HVRA, and “infrastructure” would be the Primary HVRA. The hierarchical structure is simply a convenient way to organize and summarize a long list of HVRAs.
Using HVRA Sets in IFTDSS
Deciding what to include in your HVRA set should be based on how you intend to use that set. For HVRA sets intended for Exposure Analyses or Quantitative Wildfire Risk Assessments (QWRAs), the geographic extent HVRAs selected should reflect the desired extent and components to be quantitatively evaluated and compared. For HVRA sets intended to be used primarily for visual assessment and overlaying with model outputs, the HVRAs selected can be more dynamic and exploratory.
Tip: For Exposure Analysis and Risk. When identifying which HVRAs to include in your analysis, it is important to limit the list of HVRAs to those of high value. Keeping the scope limited ensures that the interpretation of the results from your analysis remains manageable.
Tip: For Exposure Analysis and Risk. Use an LBP Model Output to set the geographic extent of your mapped values if you intend to use the resulting HVRA Set later for an Exposure Analysis or Risk Assessment. See the Geographic Extent section for more detail.
Follow the steps in the Map Values tutorial to create and view HVRA Sets in IFTDSS. When creating sets you can specify the geographic extent from a variety sources (outlined in the section below). When selecting HVRAs, you may choose to use selected IFTDSS Reference Layers, HVRA National Layers, or your own shape or shapefile.
See the HVRA Considerations topic for further information on selecting a geographic extent.
