Note: The fire behavior calculations for this model are the product of fire behavior libraries developed by the Missoula Fire Sciences Laboratory , Missoula, MT.
The IFTDSS Minimum Travel Time Fire Spread (MTT) model is identical to Minimum Travel Time (MTT) model in FlamMap, with some fixed modeling inputs (see below for details). Minimum Travel Time Fire Spread simulates head, backing and flanking fire.
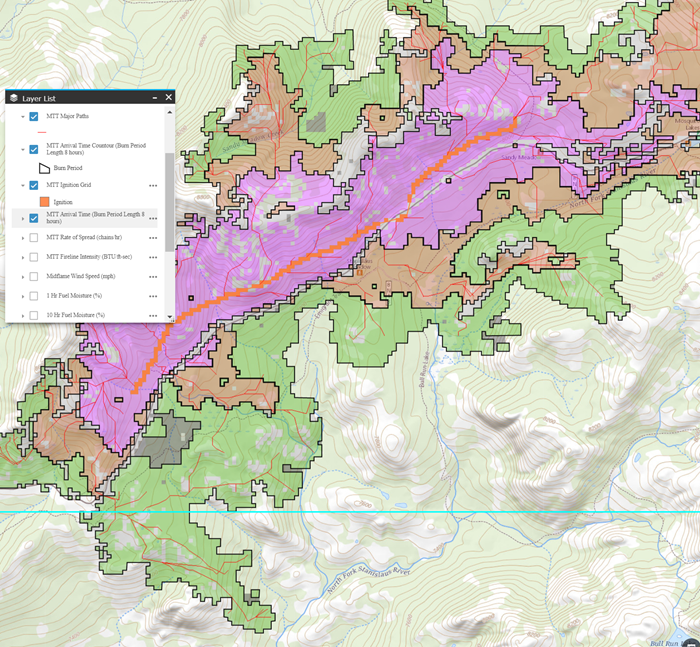
FlamMap MTT Background
FlamMap is a fire behavior mapping and analysis software application that computes potential fire behavior characteristics (such as spread rate, flame length, and fireline intensity) over an entire landscape under constant weather and fuel moisture conditions input by the user. FlamMap simulates surface and crown fire behavior characteristics using Rothermel’s 1972 surface fire model, Van Wagner’s 1977 crown fire initiation model, and Rothermel’s 1991 crown fire spread model.
The MTT part of FlamMap is a two-dimensional fire growth model. It calculates fire growth and behavior by searching for the set of pathways with minimum fire spread times from point, line or polygon ignitions. MTT simulates fire spread by Huygens’ principle where the growth and behavior of the fire edge is a vector or wave front (Richards, 1990; Finney, 2002). MTT includes heading, flanking, and backing spread. Because the MTT calculations spread under constant weather and fuel moisture conditions it enables analysis of the effects of spatial patterns in fuels and topography (Finney, 2006).
Fixed inputs in IFTDSS
Many of the model inputs are controlled by the user (see the Input Overview topic for more details); however some model inputs are fixed in IFTDSS runs and cannot be changed by the user:
-
Interval for Minimum Travel Time Paths: This controls how the program selects and outputs the MTT Major Paths at a specified distance interval, and is set to 300 m.
-
Spotting delay: The time between ember landing and initiation of fire spread is set to 0 minutes.
-
Spotting seed: The spotting seed is a randomly generated value that determines whether a specific spot causes an ignition. In IFTDSS, the spotting seed is set for the first model run for a given landscape family and ignition. Subsequent runs using the same combination re-use the spotting seed. This allows for accurate comparisons between model runs using the same landscape family and ignition. Such comparisons can be useful to test the effectiveness of fuel treatment alternatives or to compare the impacts of changing weather parameters. Were spotting seed not held constant in these scenarios, you would be unable to deduce whether changes in fire behavior were due to the changes you specified or the result of differences in spotting.